Source: Aon’s Annual Ward Report Results (1990-2021)
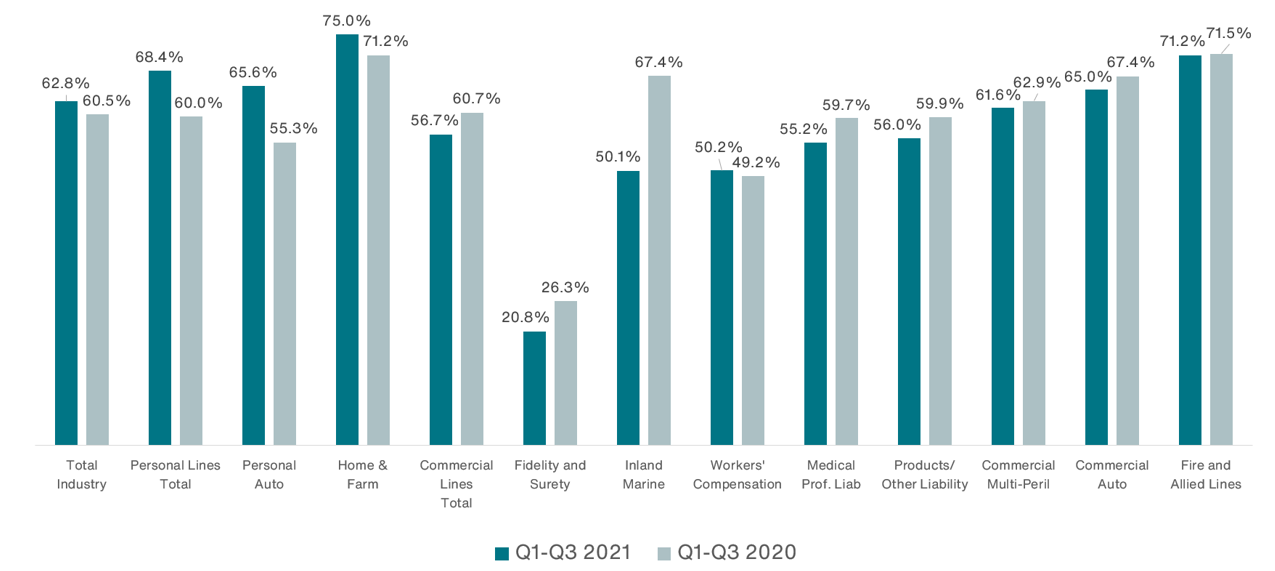
Direct loss ratios for most lines of business in 2021 had lower loss ratios throughout the first three quarters of the year compared to 2020 (Figure 2). Personal lines suffered a big upswing in loss ratios with home & farm insurance losses going up 3.8 points and auto losses going up more than 10.0 points. These increased ratios are the result of elevated catastrophe activity linked to wildfires, hurricanes and tornadoes and supply chain challenges coupled with inflation. Auto losses are less surprising when you think about the increased activity and severity out there following the loosening of pandemic-related restrictions on travel. Unlike personal lines, commercial lines went down with almost every line improving slightly except for workers’ compensation.
Figure 2 – Direct Loss Ratios
Source: Aon’s Annual Ward Report Results (2020-2021)
Human Capital Trends
Over the last few years, many companies have taken on initiatives that are driving the development of the future of work. Companies are changing the ways employees work by evaluating the skills and competencies of their talent pool and designing jobs around specific skills. This booming shift has altered the recruiting landscape and the approach of companies to hire and retain talent. Rewards are changing too, as companies look to ensure pay levels are market appropriate and based on targets aligned with the organization internally. Changes in business strategy across industries are increasingly widespread with more companies rethinking their future workforce architecture to stay competitive and resilient in the face of disruptions.
Companies continue to leverage technology, electronic communication, and social distancing to manage, retain and attract talent. The U.S. unemployment rate rested at 4.2 percent, with the insurance industry even lower at 1.4 percent. The workforce demonstrated significant resilience in the past year and the focus of companies on implementing more human capital practices remains strong as they look to rebound and grow from recent global, economic, and social disruptions.
Demand for insurance talent remains high as industry job openings increased to 263,000 in 2021 from 242,000 in 2020 (Figure 3). The semi-annual Insurance Labor Market Study, conducted in partnership with the Ward benchmarking practice at Aon and The Jacobson Group, revealed that 56.0 percent of respondents were planning to increase staff. A small 7.0 percent of respondents expected to decrease staff, down from 17.0 percent in 2020.
Over the past five years, the property-casualty industry has experienced headcount changes indicative of a shifting prioritization of key roles (Figure 3). Headcount increased most significantly for executive and corporate functions at 40.0 percent, followed by marketing and legal functions with increases at 32.0 percent and 31.0 percent, respectively. Companies are on the lookout for leadership talent capable of prioritizing business development and strategy in the face of emerging disruptions. Legal and corporate claims functions continue to grow as regulatory compliance increases and more oversight of claims is needed. Technology positions are in the greatest demand across the industry and remain a difficult area for recruiters.
Figure 3 – Percentage of Total Headcount Increases for Organization Functions (2016-2021)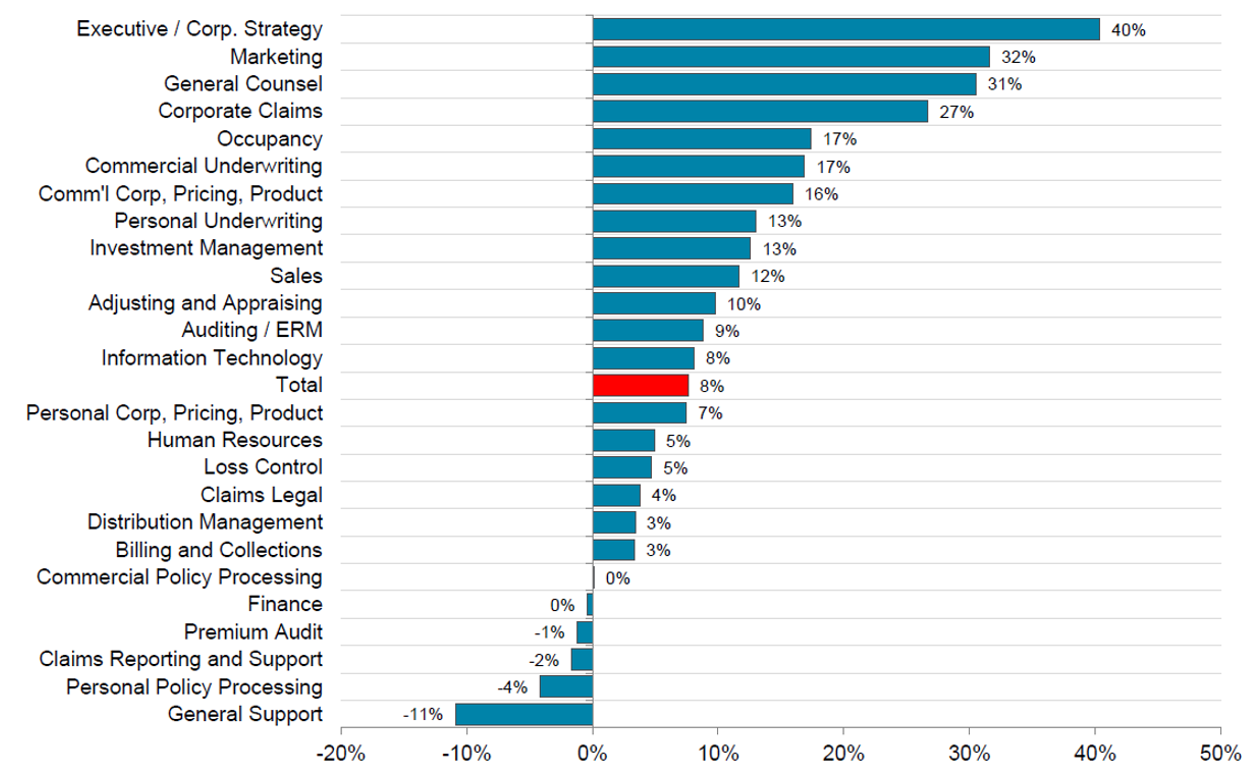
Companies are focused on experienced leadership rather than entry-level positions in many areas, such as technology, product management, underwriting, analytics, and sales, and marketing. Senior roles are in high demand and employers continue to offer robust pay increases and benefits to stay competitive.
“Many companies implemented lower increases in pay in 2020 and 2021 in response to economic uncertainty,” Jeff Rieder, a partner at Aon’s human capital business, said in our recent webcast. “We anticipate a greater increase in pay in future years in response to the labor market shortage and the demand for talent.”
Building the Digital Future
Capital flow into the insurance technology market is robust as companies rebound from social and economic disruptions. Funding volume in 2021 surpassed the funding of any previous full year for the past four years. Investments are not only being driven by the need for digital transformation; they are reinforced by the pandemic and increased customer demand for new and enhanced digital experiences. Independent agents and agency carriers are embracing mergers, acquisitions, and consolidation deals that can significantly impact distribution. Agency carriers now face challenges like paying competitive wages, maintaining an acceptable expense ratio, and focusing on agencies with the biggest opportunities for growth. As carriers’ omnichannel strategies evolve, many carriers are expanding their customer service centers.
Digital self-service is a valued market area gaining a lot of attraction according to Aon’s Ward Digital Capability and Customer Engagement Survey from Q1 2021. A vast majority of the total organizations surveyed (86.0 percent) are adapting to virtual self-service capabilities. Companies that offer these capabilities, such as viewing policy details, history, and single bill payment, will be better positioned to keep up with the competition in the market and growing customer demands for an enhanced digital experience.
Digital capabilities for policyholders continue to evolve with a quarter of survey respondents indicating that policyholders are registered for online/portal access with 34.0 percent registered for personal lines carriers and 22.0 percent for commercial lines carriers. More than a quarter of companies surveyed, 31.0 percent, offer a mobile app despite policyholder downloads remaining stagnant and below 2.0 percent.
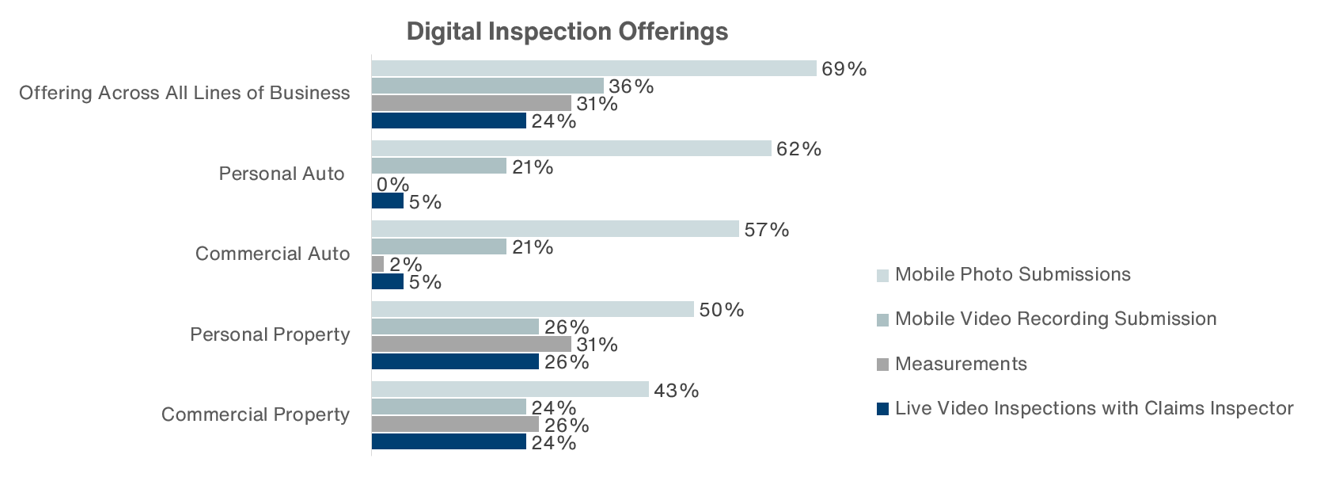
Claims technology has become one of the largest and fastest-growing operations in the insurance industry. There are more opportunities than ever for technology to help improve processes. Digital claims inspections are on the rise with 69.0 percent of carriers offering policyholder photo submissions (Figure 4). Of the companies with photo submission capability, 38.0 percent had a digital photo anti-fraud solution in place. Mobile technology and communication used to report claims is a top utilization mechanism for policyholders. Mobile loss intake and out is offered by 44.0 percent of carriers, and of those carriers, 57.0 percent had mobile claims automatically uploaded in their system.
Billing and claim payments have been slow to catch up as paper checks still dominate with an 89.0 percent utilization rate. Paperless billing adoption rates remain low at 19.0 percent despite 57.0 percent of companies surveyed offering paperless billing.
Figure 4 – Claims Digital Capabilities
Source: Aon’s Ward Digital Capability and Customer Engagement Survey, March 2021
As technology capabilities grow, companies and industries are increasingly prone to cyber risks and challenges. Costs of ransomware attacks increased in the past five years from 15,000 to 175,000 as ransomware attacks become more common. The average cyber insurance premium is expected to increase between 35.0 to 40.0 percent from 2020 to 2021.
Information security expense as a percent of premiums was 0.17 percent. Commercial carriers had the lowest expense ratio at 0.14 percent. The average was similar when analyzed by company size, as the small and large benchmarks both average at 0.17 percent. Top concerns for companies regarding information security include the prevention of future cyber threats, end-user information security training, and managing third-party and cloud security risks. Investments in information security represented 5.0 percent of the total information technology budget in 2020, on average. Cyber insurance and risk services including security audits, consulting, and computing hardware are also expected to rise in cost in the coming years as new disruptions emerge. Companies are likely to invest more and dedicate greater resources to mitigate cyber and information security disruptions and prepare for a more digital future.
Next Steps
The year ahead promises disruption from the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic to prolonged inflation and economic and labor volatility, but companies can take proactive action now to mitigate the impact and stay resilient in 2022.
In order to lay the groundwork to enable greater workforce resilience and agility going forward, companies should remain flexible on where work gets done to attract and retain talent. As technology and function costs increase, companies need to consider investments in hiring, benefits, and incentives during a period of aggressive activity and a labor market shortage.
Companies should focus on the digital transformation of their capabilities when it comes to programs and beyond given increased customer demands for a more digital experience. It’s vital that organizations not only understand the cyber and information technology risks out there but also the importance of investment in new technology.
Companies that adopt and accelerate progress on these and other workforce trends will be increasingly competitive in the market, resilient to severe disruption, and better positioned to achieve talent attraction and retention goals in the year ahead.